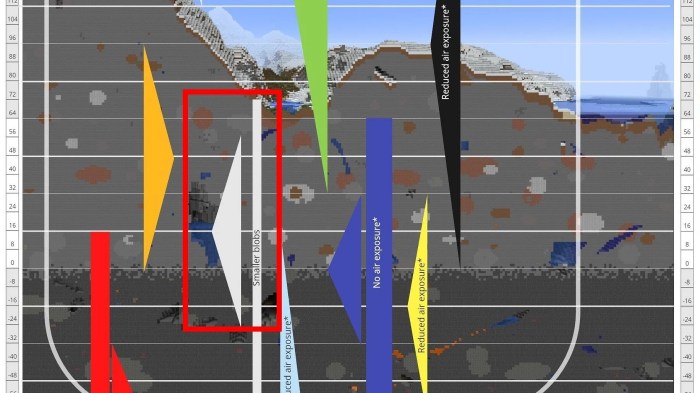
What level to mine iron – When it comes to mining iron, knowing the optimal level can make all the difference. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of iron mining, exploring the ideal locations, effective methods, essential tools, and crucial environmental considerations. Whether you’re a seasoned miner or just starting out, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge and insights to maximize your iron mining endeavors.
Iron Mining: A Comprehensive Guide: What Level To Mine Iron
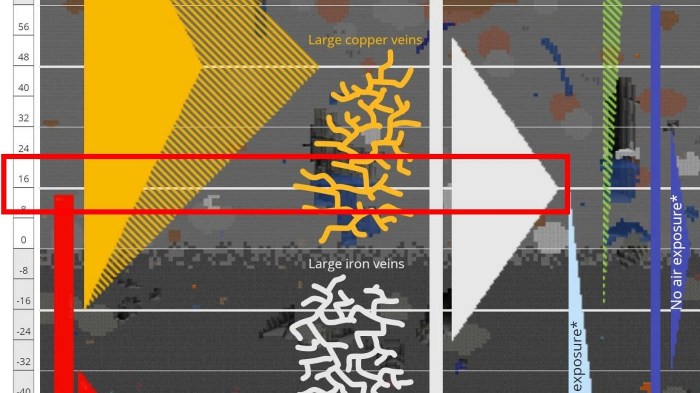
Iron, an essential element in our modern world, is extracted from the earth through a process known as mining. This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of iron mining, providing insights into the techniques, tools, and environmental considerations involved in this industry.
Mining Locations, What level to mine iron

The choice of mining location depends on the availability of iron ore deposits and the accessibility of the site. Surface mining, underground mining, and cave mining are the primary methods used to extract iron ore.
| Location | Accessibility | Yield | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Mining | Easy | Moderate | High |
| Underground Mining | Difficult | High | Low |
| Cave Mining | Moderate | Low | Medium |
Mining Methods

- Open-pit Mining:Involves removing the overburden (soil and rock) to expose the iron ore deposit. This method is suitable for large, near-surface deposits.
- Underground Mining:Accessing the iron ore deposit through tunnels and shafts. This method is used for deep deposits or when surface mining is not feasible.
- Placer Mining:Extracting iron ore from loose sediments, often found in riverbeds or glacial deposits. This method is suitable for small-scale operations.
Tools and Equipment
| Category | Tools |
|---|---|
| Excavation | Picks, shovels, backhoes |
| Drilling | Drills, drill bits |
| Blasting | Explosives, detonators |
Safety precautions, such as wearing protective gear and following proper handling procedures, are crucial when using these tools.
Iron Ore Properties
Iron ore is primarily composed of iron oxides, such as hematite and magnetite. Its density ranges from 4.5 to 5.3 g/cm³, and its hardness varies from 5 to 6 on the Mohs scale.
| Property | Significance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Determines the iron content and purity of the ore. |
| Density | Affects the ease of transportation and processing. |
| Hardness | Influences the mining methods and extraction techniques. |
Environmental Considerations

- Land Disturbance:Mining activities can result in deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat loss.
- Water Pollution:Mining runoff can contaminate water sources with heavy metals and sediments.
- Air Emissions:Blasting and ore processing can release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
Best practices and regulations are implemented to mitigate these impacts, such as land reclamation, water treatment, and air pollution control.
FAQ Section
What are the most common methods used to mine iron?
The primary methods employed in iron mining include open-pit mining, underground mining, and placer mining.
What factors should be considered when determining the ideal mining level?
Accessibility, yield, and safety are crucial factors to evaluate when selecting the optimal mining level.
What environmental concerns are associated with iron mining?
Iron mining can lead to land disturbance, water pollution, and air emissions, necessitating the implementation of best practices and regulations to mitigate these impacts.