Delve into the intricate world of Legend of Zelda NES maps, where exploration and discovery intertwine. From the sprawling overworld to hidden passages, this guide unravels the secrets and strategies concealed within the game’s iconic maps.
Navigate through detailed descriptions of key landmarks, dungeon layouts, and item placement. Uncover the significance of secret areas and hidden passages, and witness the evolution of maps as you progress through the story. Prepare to enhance your gameplay and rediscover the magic of Legend of Zelda with this comprehensive guide to its captivating maps.
Overworld Map: Legend Of Zelda Nes Maps
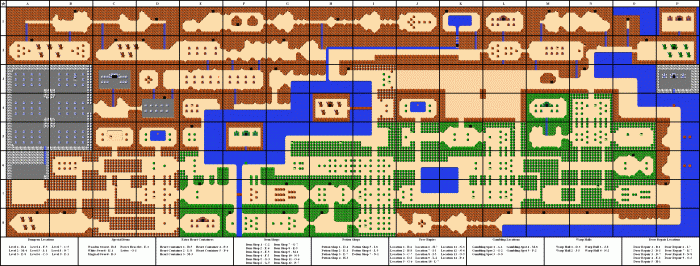
The overworld map in The Legend of Zelda is a sprawling and diverse landscape, spanning forests, deserts, mountains, and oceans. It is divided into nine distinct regions, each with its own unique landmarks and challenges.
The map is connected by a network of paths and bridges, allowing players to travel between regions with ease. The overworld is also dotted with towns and dungeons, which offer opportunities for rest, supplies, and adventure.
The geographical diversity of the overworld map is one of its most striking features. The lush forests of Hyrule Field contrast sharply with the barren deserts of the Death Mountain range. The towering peaks of Death Mountain provide a dramatic backdrop to the game, while the vast oceans offer a sense of mystery and adventure.
Dungeon Maps, Legend of zelda nes maps

| Dungeon Name | Location | Boss | Key Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| Death Mountain | Death Mountain range | Dodongo | Bow |
| Zora’s Domain | Zora’s River | King Zora | Flippers |
| Ice Palace | Death Mountain range | Kholdstare | Ice Rod |
| Desert Palace | Desert of Hyrule | Moldorm | Book of Mudora |
| Skull Woods | Lost Woods | Ganon | Triforce of Courage |
| Thieves’ Town | Hyrule Field | Agahnim | Magic Mirror |
| Tower of Hera | Death Mountain range | Agahnim | Master Sword |
| Ganon’s Tower | Death Mountain range | Ganon | Triforce of Wisdom |
The dungeons in The Legend of Zelda are complex and challenging, each with its own unique layout, puzzles, and enemies. Players must use their wits and skills to navigate the dungeons, defeat the bosses, and collect the key items necessary to progress through the game.
Item Placement
The placement of items in The Legend of Zelda is carefully designed to encourage exploration and reward players for their efforts. Key items, such as the Bow and the Master Sword, are often hidden in difficult-to-reach locations or guarded by powerful enemies.
The strategic placement of items also influences the way players approach the game. For example, the Bow is essential for defeating Dodongo, the boss of Death Mountain. However, players must first find the Bow before they can challenge Dodongo.
Secret Areas and Hidden Passages

The Legend of Zelda is full of secret areas and hidden passages that offer rewards for exploration. These hidden locations can be found by examining the overworld map carefully or by talking to NPCs.
One of the most famous secret areas in The Legend of Zelda is the Lost Woods. The Lost Woods is a maze-like forest that can be difficult to navigate. However, players who can find their way through the Lost Woods will be rewarded with the Master Sword, the most powerful weapon in the game.
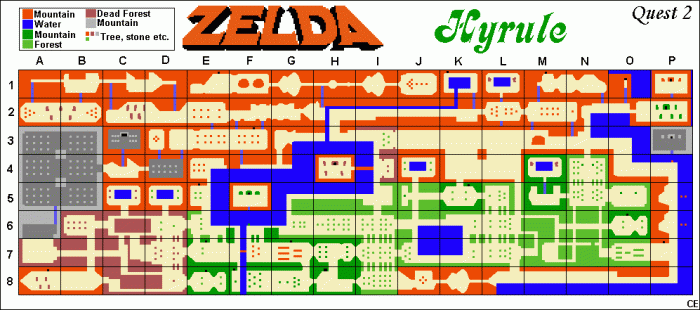
Map Evolution and Progression

The overworld map in The Legend of Zelda evolves as the player progresses through the game. New areas become accessible as players acquire new items and abilities. For example, the Desert of Hyrule is inaccessible until players acquire the Book of Mudora.
The map progression in The Legend of Zelda is carefully designed to pace the game and ensure that players are always challenged but never overwhelmed. The game’s world gradually opens up as players become more powerful, allowing them to explore new areas and face new challenges.
Map Design and Aesthetics
The overworld map in The Legend of Zelda is a beautiful and iconic work of art. The map is drawn in a simple but effective style, with vibrant colors and clear lines. The map is also full of small details, such as trees, mountains, and rivers, that bring the world to life.
The map design in The Legend of Zelda is also functional. The map is easy to read and navigate, and it provides players with a clear sense of their location in the world. The map also uses color and symbols to indicate important locations, such as towns, dungeons, and secret areas.
FAQ Compilation
What is the significance of the overworld map in Legend of Zelda?
The overworld map provides a comprehensive overview of Hyrule, connecting different regions and highlighting key landmarks. Its geographical diversity and environmental variations influence gameplay and enhance the sense of exploration.
How are dungeons incorporated into the game’s maps?
Dungeons are distinct locations within the overworld, each with its unique layout, challenges, and rewards. They are strategically placed to guide the player’s progression and offer valuable items essential for completing the game.
What role does item placement play in Legend of Zelda?
Item placement is crucial to the game’s strategy. Key items are carefully positioned throughout the maps, influencing gameplay and shaping the player’s journey. Discovering and utilizing these items effectively is essential for overcoming obstacles and progressing through the game.
How do secret areas enhance the exploration experience?
Secret areas and hidden passages offer a sense of discovery and reward. They are often concealed within the maps, requiring careful observation and exploration to uncover. Accessing these areas can lead to valuable items, unique challenges, or shortcuts, enhancing the overall gameplay experience.
How does map evolution reflect the player’s progress?
As the player progresses through the story, new areas become accessible, and the maps adapt to reflect their journey. This evolution of maps not only provides navigational guidance but also serves as a visual representation of the player’s accomplishments and the unfolding narrative.