ksp delta v for orbit is a fundamental concept in orbital mechanics, determining the amount of velocity change required to insert a spacecraft into orbit. This guide will delve into the intricacies of delta-v, its relationship with specific impulse, and practical applications in Kerbal Space Program (KSP).
By understanding delta-v requirements and optimizing maneuver execution, you’ll unlock the secrets of efficient and precise orbital insertions, enabling you to conquer the celestial frontiers in KSP and beyond.
Delta-v Requirements for Orbit Insertion
Delta-v, or change in velocity, is a crucial concept in orbital maneuvers. It represents the amount of velocity that must be applied to a spacecraft to change its orbit. The delta-v required for orbit insertion is determined by the target orbit’s altitude, inclination, and eccentricity.
The formula for calculating delta-v for orbit insertion is:
Δv = √(v_f^2
v_i^2)
where:
- Δv is the delta-v required for orbit insertion
- v_f is the final velocity in the target orbit
- v_i is the initial velocity in the current orbit
The factors that influence delta-v requirements include:
- Orbit altitude:Higher orbits require more delta-v to achieve.
- Orbit inclination:Changing the inclination of an orbit requires additional delta-v.
- Orbit eccentricity:Eccentric orbits require more delta-v to achieve than circular orbits.
Specific Impulse and Delta-v
Specific impulse (Isp) is a measure of the efficiency of a rocket engine. It is defined as the amount of thrust produced per unit of propellant mass. The relationship between Isp and delta-v is given by the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation:
Δv = Isp
- g
- ln(m_i/m_f)
where:
- Δv is the delta-v
- Isp is the specific impulse
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- m_i is the initial mass of the spacecraft (including propellant)
- m_f is the final mass of the spacecraft (after propellant consumption)
The trade-offs between Isp and propellant mass for different mission scenarios must be considered. High Isp engines are more efficient but may require more propellant, while low Isp engines are less efficient but may require less propellant.
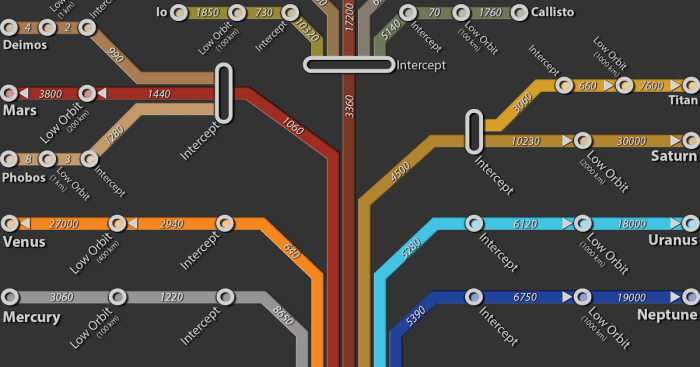
Delta-v Budgets for KSP
In Kerbal Space Program (KSP), delta-v budgets are essential for mission planning and execution. The following table provides typical delta-v budgets for different orbits in KSP:
| Orbit | Delta-v (m/s) |
|---|---|
| Low Kerbin Orbit (100 km) | 3500 |
| Munar Orbit | 6500 |
| Minmus Orbit | 5000 |
| Jool Orbit | 12000 |
These budgets should be considered as guidelines, and actual delta-v requirements may vary depending on the specific mission parameters.
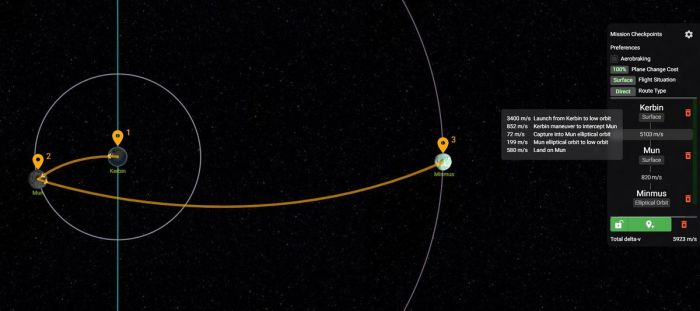
Maneuver Planning and Execution

Planning and executing orbital maneuvers in KSP requires careful consideration. The following steps are recommended:
- Plan the maneuver:Use the maneuver node editor to create a maneuver node and adjust the delta-v and direction of the burn.
- Execute the maneuver:Once the maneuver node is set, execute the burn by applying thrust in the desired direction.
- Monitor the burn:Use the Navball and other instruments to monitor the burn progress and make any necessary adjustments.
- Fine-tune the orbit:After the initial burn, fine-tune the orbit using small burns to achieve the desired precision.
Real-World Applications of Delta-v: Ksp Delta V For Orbit

Delta-v calculations are essential in real-world space missions. For example:
- The Apollo 11 mission required a delta-v of approximately 12,000 m/s to achieve lunar orbit.
- The Cassini-Huygens mission required a delta-v of approximately 17,000 m/s to reach Saturn’s orbit.
- The Mars Curiosity rover required a delta-v of approximately 6,000 m/s to land on Mars.
Delta-v budgeting is crucial in mission design and execution, as it ensures that spacecraft have sufficient fuel to complete their missions successfully.
Query Resolution
What is delta-v?
Delta-v is the change in velocity required to perform orbital maneuvers, such as orbit insertion, inclination changes, and rendezvous.
How do I calculate delta-v for orbit insertion?
Delta-v for orbit insertion depends on factors like orbit altitude, inclination, and eccentricity. Formulas and equations are available to calculate the exact delta-v.
What is the relationship between specific impulse and delta-v?
Specific impulse (Isp) measures the efficiency of a rocket engine. Higher Isp means less propellant mass is required to achieve a given delta-v.