How to make an iron block – Embark on a journey into the captivating world of iron block making. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricate processes involved, from extracting iron ore to forging and shaping the final product. Immerse yourself in the fascinating history, techniques, and applications of this essential material.
Iron blocks, with their exceptional strength and durability, have played a pivotal role in shaping human civilization. From ancient tools to modern machinery, their versatility and resilience have made them indispensable in countless industries. Understanding the intricacies of their creation not only provides valuable knowledge but also fosters an appreciation for the craftsmanship and ingenuity behind these remarkable objects.
Materials and Equipment
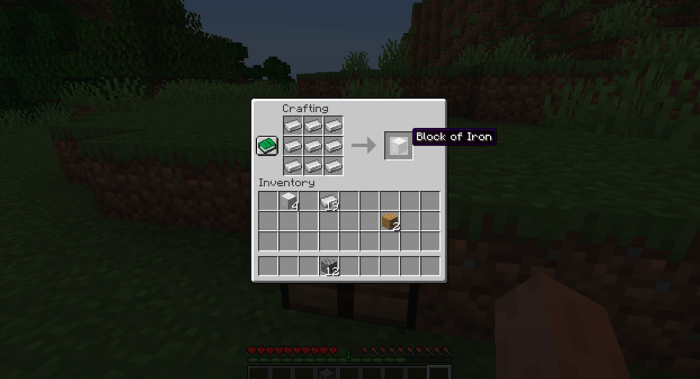
To craft an iron block, gather the following materials and equipment:
- Iron ore
- Coke (a fuel derived from coal)
- Limestone (a flux that removes impurities)
Essential equipment includes:
- Blast furnace (a tall, cylindrical furnace used to smelt iron ore)
- Crucible (a container for molten iron)
- Mold (a form for shaping the molten iron)
- Forge (a furnace for heating iron)
- Anvil (a heavy block used for shaping iron)
- Hammer
Safety Precautions

Working with molten iron poses significant hazards. Observe these safety guidelines:
- Wear protective clothing, including a heat-resistant suit, gloves, and boots.
- Use a respirator to prevent inhaling toxic fumes.
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Never touch molten iron with bare hands.
Preparation of Iron Ore
Iron ore, extracted from natural sources like mines, contains impurities. To obtain pure iron, the ore undergoes the following steps:
- Crushing: The ore is crushed into smaller pieces.
- Beneficiation: The crushed ore is separated from impurities using techniques like magnetic separation.
- Roasting: The ore is heated to remove moisture and drive off volatile impurities.
- Sintering: The roasted ore is agglomerated into lumps to improve its strength and reduce porosity.
The chemical reactions involved in these processes include:
Fe2O 3+ 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO 2(Reduction of iron oxide by carbon monoxide)
Smelting and Casting

Smelting is the process of converting iron ore into molten iron. It takes place in a blast furnace, where the ore, coke, and limestone are fed from the top. Hot air is blown into the furnace from the bottom, creating a high temperature that melts the iron ore.
The molten iron, known as pig iron, collects at the bottom of the furnace and is tapped off.
Casting involves pouring molten iron into a mold to create the desired shape. The mold is typically made of sand or a refractory material that can withstand the high temperature of the molten iron.
Forging and Shaping: How To Make An Iron Block

Forging is the process of shaping iron by heating it and hammering it into the desired form. The iron is heated in a forge until it becomes pliable, then it is placed on an anvil and hammered into shape.
Various forging techniques are used, including:
- Upsetting: Increasing the thickness of a piece of iron by hammering it on the end.
- Drawing out: Lengthening a piece of iron by hammering it on the sides.
- Bending: Changing the angle of a piece of iron by hammering it over a form.
- Twisting: Creating a spiral or helical shape by twisting a piece of iron.
Finishing and Polishing
Finishing and polishing give the iron block its final appearance and protect it from corrosion.
Finishing methods include:
- Sanding: Smoothing the surface of the iron block with sandpaper.
- Grinding: Removing excess material and shaping the block using a grinding wheel.
- Polishing: Creating a smooth, shiny surface using a polishing compound.
The choice of finishing method depends on the desired surface finish.
Common Queries
What is the primary use of iron blocks?
Iron blocks are primarily used in construction, engineering, and manufacturing industries due to their exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear.
Can iron blocks be recycled?
Yes, iron blocks can be recycled and reused multiple times without losing their inherent properties, making them an environmentally sustainable material.
What are the key safety precautions to consider when working with molten iron?
When working with molten iron, it is crucial to wear appropriate protective gear, including heat-resistant clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Proper ventilation and adherence to safety protocols are also essential to minimize risks.