Embark on a journey into the world of lumber production with our comprehensive guide, “How to Build a Sawmill.” This insightful resource will empower you with the knowledge and expertise to establish a thriving sawmill operation, transforming raw logs into valuable lumber.
From site selection and equipment procurement to log processing and lumber finishing, we’ll delve into every aspect of sawmill construction and operation, ensuring you possess the confidence and skills to navigate this industry successfully.
Planning and Preparation
Effective sawmill operations begin with meticulous planning and preparation. This involves selecting a suitable site, acquiring the necessary land, and securing permits and licenses. A comprehensive business plan Artikels operational goals, market analysis, and financial projections.
Site Selection and Land Acquisition
- Proximity to timber resources
- Access to transportation routes
- Availability of water and electricity
- Adequate land for sawmill operations and log storage
Permits and Licenses
- Environmental permits for air and water quality
- Building permits for construction
- Business licenses for operation
Business Plan Development

- Market analysis: Identify target customers, competition, and market trends
- Operational plan: Define production capacity, equipment needs, and staffing requirements
- Financial plan: Project costs, revenue, and profitability
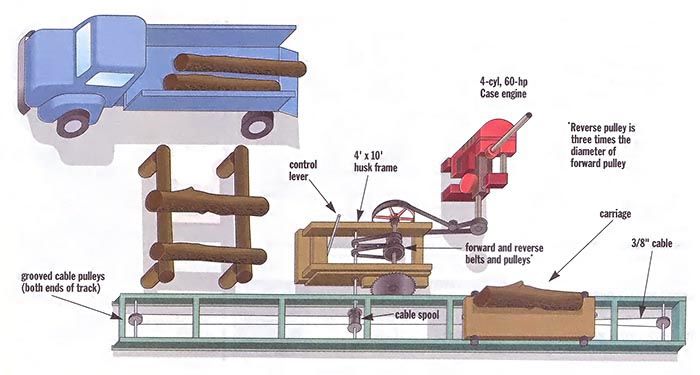
Equipment Selection and Layout
The choice of sawmill equipment depends on the type of logs being processed, desired production capacity, and available budget. Proper layout optimizes workflow and efficiency.
Essential Equipment
- Log deck and conveyors
- Debarker
- Sawmill headrig
- Edger
- Trimmer
Types of Saws
- Band saws: Continuous blade for precise cuts
- Circular saws: Single blade for high-speed cutting
- Chainsaws: Portable for felling and bucking
Sawmill Layout
- Log flow from deck to headrig
- Edger and trimmer placement for efficient lumber flow
- Waste handling and disposal
Raw Material Acquisition and Processing
Sawmills rely on a steady supply of logs. Sourcing, handling, and processing logs impact lumber quality and efficiency.
Log Sourcing

- Identify and contract with timber suppliers
- Establish specifications for log size, quality, and species
- Secure transportation arrangements
Log Handling and Storage
- Log deck for unloading and sorting
- Log yard for storage and inventory management
- Proper stacking and protection from elements
Debarking and Sawing Techniques
- Debarking removes bark to improve lumber quality
- Headrig cuts logs into lumber of desired dimensions
- Edging and trimming refine lumber size and shape
Lumber Drying and Finishing
Lumber drying stabilizes moisture content, reduces warping, and improves durability. Finishing processes enhance appearance and functionality.
Drying Methods
- Air drying: Natural process using outdoor conditions
- Kiln drying: Controlled environment for faster and more precise drying
Moisture Content and Kiln Schedules
- Target moisture content for different lumber species
- Kiln schedules control temperature and humidity to achieve desired moisture levels
Lumber Grading and Finishing Techniques
- Grading based on quality and appearance
- Planing to smooth surfaces
- Sanding to remove imperfections
Safety and Maintenance
Sawmills pose inherent hazards, necessitating strict safety protocols and regular equipment maintenance.
Safety Protocols, How to build a sawmill
- Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Machine guards and safety devices
- Training and safety awareness programs
Equipment Maintenance
- Regular inspections and lubrication
- Scheduled maintenance to prevent breakdowns
- Troubleshooting and repair procedures
Marketing and Sales
Sawmills need to establish a strong market presence to sell lumber effectively.
Market Research and Customer Identification
- Identify potential customers in construction, furniture, and other industries
- Analyze market trends and competition
Marketing Strategies
- Develop brand identity and marketing materials
- Establish online presence and social media engagement
- Attend industry events and trade shows
Sales Channels and Pricing Considerations
- Direct sales to customers
- Wholesale distribution through brokers
- Pricing based on lumber grade, species, and market demand
FAQ Explained: How To Build A Sawmill
What is the most important factor to consider when selecting a site for a sawmill?
Access to a reliable supply of high-quality logs is paramount.
What type of saw is most suitable for a small-scale sawmill?
A circular saw or a band saw is commonly used for small-scale operations.
How do I ensure the safety of my sawmill operation?
Adhere to industry-standard safety protocols, provide proper training to employees, and conduct regular equipment inspections.
