Unveiling the Growth Stages of Carrots: A Journey from Seed to Harvest, this guide provides an in-depth exploration of the fascinating developmental journey of this beloved root vegetable. From the initial stages of seed germination to the final harvest, we delve into the intricate processes that shape the growth and maturation of carrots, offering valuable insights for gardeners and enthusiasts alike.
As the carrot embarks on its life cycle, it undergoes distinct stages, each characterized by unique morphological and physiological changes. Understanding these stages is crucial for optimizing cultivation practices, ensuring optimal yields, and appreciating the intricate beauty of plant growth.
Growth Stages of Carrots
Carrots ( Daucus carota) are a widely cultivated root vegetable known for their sweet, crunchy texture and nutritional value. The growth stages of carrots involve several distinct phases, each characterized by specific morphological and physiological changes. This article provides an overview of the key growth stages of carrots, from seed germination to maturity and harvesting.
Seed Germination
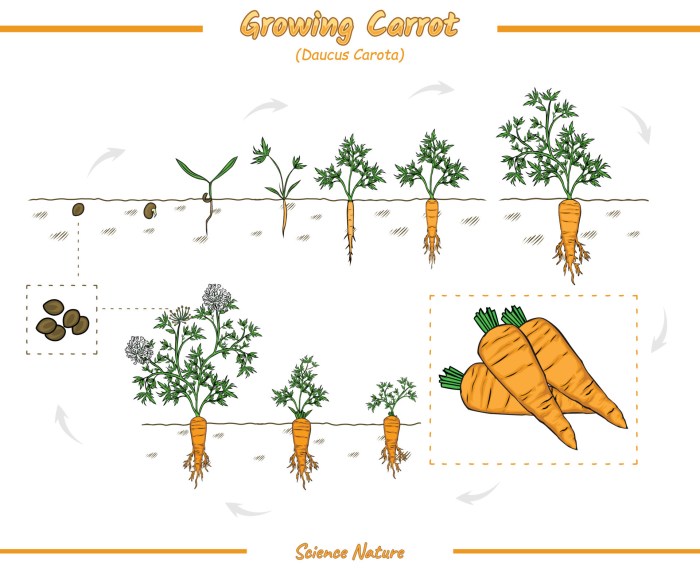
Seed germination is the initial stage of carrot growth and occurs when favorable environmental conditions are met. The ideal temperature for carrot seed germination ranges from 60-70°F (15-21°C). The seeds require adequate moisture and oxygen to initiate the process of imbibition, during which water is absorbed by the seed coat.
This process activates enzymes within the seed that break down stored food reserves, providing energy for radicle emergence.
Seedling Growth

Once the radicle emerges from the seed coat, the seedling stage begins. During this phase, the carrot seedling undergoes rapid growth and development. The cotyledons, or seed leaves, emerge and expand, providing photosynthetic capacity for the young plant. The hypocotyl, or stem, elongates, and the first true leaves develop.
Light and water play crucial roles in seedling growth, providing energy and nutrients for the developing plant.
Root Development
Root development in carrots involves several distinct stages. The primary root emerges from the radicle and grows downward, anchoring the plant in the soil. Secondary roots develop from the primary root and form a network that absorbs water and nutrients from the soil.
The elongation of roots is regulated by auxins, plant hormones that promote cell division and growth. Various factors, including soil conditions, moisture levels, and nutrient availability, influence root growth and development.
Tuberization, Growth stages of carrots

Tuberization is a unique growth stage in carrots where the taproot swells and develops into a fleshy, edible storage organ. This process is initiated by environmental cues, such as day length and temperature. Gibberellins, a type of plant hormone, play a crucial role in tuber initiation and growth.
The accumulation of sugars and starch within the root cells contributes to the enlargement and development of the carrot tuber.
Maturity and Harvesting

Carrot maturity is characterized by specific morphological and physiological changes. The roots reach their full size and develop a deep orange color due to the accumulation of carotenoids. The leaves turn yellow and senesce as the plant diverts resources to the storage root.
Harvesting time is critical to ensure optimal carrot quality and storage potential. Carrots should be harvested when they reach maturity, as over-mature roots may become fibrous and lose their flavor.
Questions Often Asked
How long does it take for carrots to grow?
The growth period of carrots varies depending on the variety, but typically ranges from 60 to 120 days.
What is the optimal soil pH for growing carrots?
Carrots prefer well-drained, sandy loam soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8.
How often should carrots be watered?
Carrots require regular watering, especially during the early stages of growth. Water deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
What are the common pests and diseases that affect carrots?
Common pests include carrot flies, aphids, and carrot rust flies. Diseases include leaf spot, blight, and root rot.
How can I improve the sweetness of my carrots?
Allowing carrots to mature fully and providing adequate sunlight can enhance their sweetness.
