Introducing the Dwarf Fortress water wheel, a versatile tool that harnesses the power of water to drive your fortress’s industries and machinery. From grinding grain to powering workshops, this guide delves into the intricacies of water wheel design, construction, and optimization, empowering you to unlock the full potential of this ancient technology in your Dwarf Fortress endeavors.
As you venture into the depths of this guide, you’ll discover the historical roots of water wheels, the key components that make them work, and practical tips for building your own water wheel using readily available materials. Explore the diverse applications of water wheels throughout history and in modern times, from powering early settlements to generating renewable energy.
Water Wheel Overview
A water wheel is a machine that converts the energy of flowing water into mechanical energy. It consists of a large wheel with buckets or paddles attached to its rim. As the water flows past the wheel, it fills the buckets and causes the wheel to turn.
The turning wheel can then be used to power other machinery, such as a millstone or a pump.
Water wheels have been used for centuries to power a variety of devices. They were first developed in the Middle East around 400 BC, and they were later adopted by the Greeks and Romans. Water wheels were used to grind grain, pump water, and power sawmills and other machinery.
In the 19th century, water wheels were replaced by steam engines and other more efficient power sources, but they are still used today in some parts of the world.
Types of Water Wheels, Dwarf fortress water wheel
- Undershot water wheelsare the simplest type of water wheel. They are placed in a stream or river, and the water flows past the bottom of the wheel, filling the buckets and causing the wheel to turn.
- Overshot water wheelsare more efficient than undershot water wheels. They are placed in a stream or river, and the water flows over the top of the wheel, filling the buckets and causing the wheel to turn.
- Breastshot water wheelsare a hybrid of undershot and overshot water wheels. They are placed in a stream or river, and the water flows into the middle of the wheel, filling the buckets and causing the wheel to turn.
Water Wheel Design and Construction

The key components of a water wheel are the axle, spokes, and buckets. The axle is the central shaft of the wheel, and the spokes are the radial beams that connect the axle to the rim of the wheel. The buckets are attached to the rim of the wheel, and they are designed to catch the water and cause the wheel to turn.
The efficiency of a water wheel is determined by a number of factors, including the diameter of the wheel, the shape of the buckets, and the speed of the water flow. The larger the wheel, the more water it can catch, and the more power it can generate.
The shape of the buckets also affects the efficiency of the wheel. Buckets that are curved or angled will catch more water than flat buckets. The speed of the water flow also affects the efficiency of the wheel. The faster the water flows, the more power the wheel can generate.
Water wheels can be built from a variety of materials, including wood, metal, and plastic. The most common type of water wheel is made from wood. Wood is a strong and durable material that is easy to work with. Metal water wheels are more expensive than wood water wheels, but they are more durable and can be used in faster-flowing water.
Plastic water wheels are the least expensive type of water wheel, but they are not as durable as wood or metal water wheels.
Water Wheel Applications
Water wheels have been used for centuries to power a variety of devices, including mills, pumps, and sawmills. In the Middle Ages, water wheels were used to grind grain into flour. In the 19th century, water wheels were used to pump water from mines and to power factories.
Today, water wheels are still used in some parts of the world to generate electricity.
Water wheels are a renewable energy source. They do not produce any emissions, and they can be used to generate electricity in remote areas where there is no access to the grid. Water wheels are also a relatively inexpensive way to generate electricity.
They can be built from locally available materials, and they require very little maintenance.
Water Wheel Efficiency and Optimization: Dwarf Fortress Water Wheel

The efficiency of a water wheel is determined by a number of factors, including the diameter of the wheel, the shape of the buckets, and the speed of the water flow. The larger the wheel, the more water it can catch, and the more power it can generate.
The shape of the buckets also affects the efficiency of the wheel. Buckets that are curved or angled will catch more water than flat buckets. The speed of the water flow also affects the efficiency of the wheel. The faster the water flows, the more power the wheel can generate.
There are a number of ways to optimize the efficiency of a water wheel. One way is to use guide vanes. Guide vanes are stationary blades that are placed in front of the wheel. They help to direct the water into the buckets, which increases the efficiency of the wheel.
Another way to optimize the efficiency of a water wheel is to adjust the angle of attack. The angle of attack is the angle at which the water strikes the buckets. The optimal angle of attack is typically between 15 and 25 degrees.
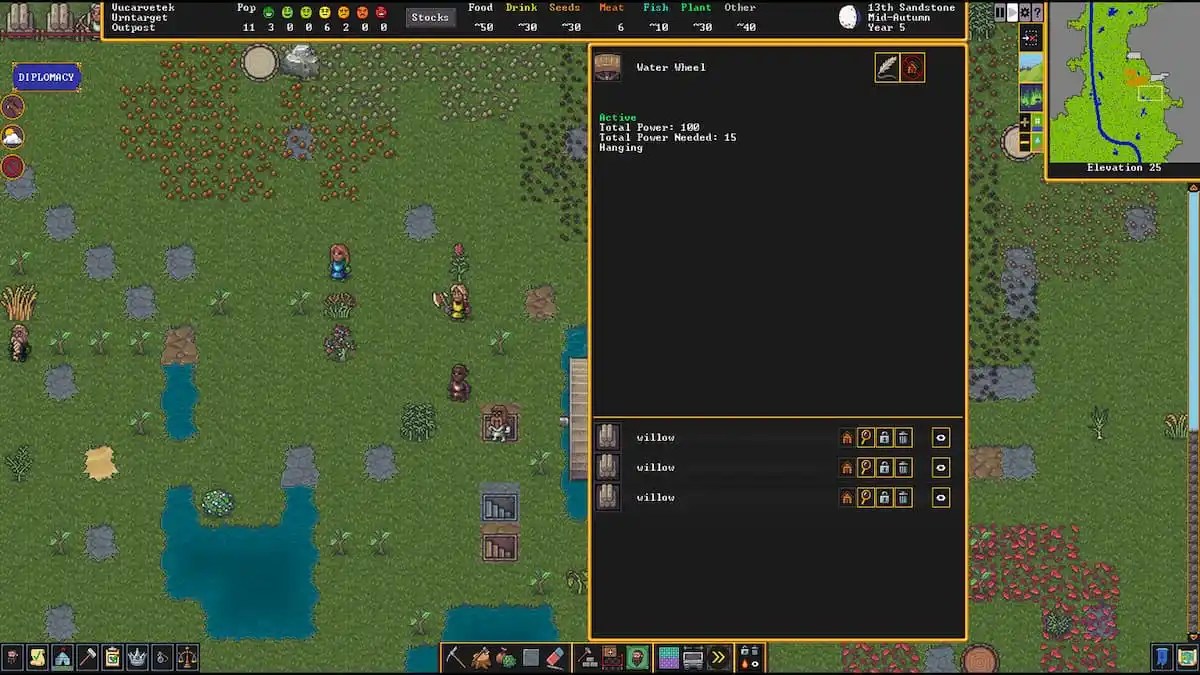
Water Wheel in Dwarf Fortress
Water wheels are a versatile and useful tool in Dwarf Fortress. They can be used to generate power, pump water, and mill flour. Water wheels are relatively easy to build, and they can be a valuable addition to any fortress.
To build a water wheel, you will need to first find a suitable location. The location should have a steady flow of water, and it should be close to the area where you want to use the power. Once you have found a suitable location, you will need to build a water wheel mechanism.
The water wheel mechanism is made up of a wheel, an axle, and a set of gears. The wheel is made of wood, and the axle is made of metal. The gears are used to connect the wheel to the device that you want to power.
Once you have built the water wheel mechanism, you will need to attach it to the water source. You can do this by building a channel or a pipe that directs the water to the wheel. Once the water wheel is attached to the water source, it will start to turn.
The turning wheel will power the device that you have connected to it.
Water wheels are a valuable addition to any Dwarf Fortress. They can be used to generate power, pump water, and mill flour. Water wheels are relatively easy to build, and they can be a valuable addition to any fortress.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary purpose of a water wheel in Dwarf Fortress?
Water wheels in Dwarf Fortress are primarily used to generate power, which can be harnessed to drive various machines and mechanisms within your fortress, such as millstones for grinding grain or bellows for powering forges.
How do I construct a water wheel in Dwarf Fortress?
To construct a water wheel in Dwarf Fortress, you will need to gather the necessary materials, including wood, metal, and leather. Once you have the materials, you can follow the step-by-step instructions provided in the game’s help menu to assemble the water wheel.
What factors affect the efficiency of a water wheel in Dwarf Fortress?
The efficiency of a water wheel in Dwarf Fortress is influenced by several factors, including the flow rate of the water, the diameter of the wheel, and the shape of the buckets. A higher flow rate, a larger wheel diameter, and optimally shaped buckets will all contribute to increased efficiency.